A Detailed Look at Motion Sensors: Types and Their Applications
Published by Amitabh Verma on 19th Sep 2024
Have you ever considered how your home security system detects an approaching presence? Motion sensors are the unsung heroes behind this technology, revolutionizing the way we interact with our surroundings. These clever devices detect movement in their vicinity, triggering responses that range from turning on lights to alerting security systems. Motion sensors have become an integral part of our daily lives, enhancing safety, convenience, and energy efficiency in countless applications.
From ultrasonic sensors to infrared technology, the world of motion detection is diverse and fascinating. This article delves into the various types of motion sensors, including PIR sensors, microwave sensors, and accelerometers. We'll explore how these devices work, their unique advantages, and the wide range of applications they serve. Whether it's in smartphone technology, automotive safety systems, or industrial automation, motion sensors are shaping the future of smart, responsive environments.
Types of Motion Sensors
Motion sensors have become an integral part of our daily lives, enhancing safety, convenience, and energy efficiency in countless applications. These clever devices detect movement in their vicinity, triggering responses that range from turning on lights to alerting security systems. Let's explore the various types of motion sensors and their unique characteristics.
Passive Infrared (PIR) Sensors
Passive infrared sensors are the most common type of motion sensors used in security systems and automated lighting. These sensors detect changes in infrared radiation emitted by living beings and objects warmer than absolute zero. PIR sensors are particularly effective at detecting human and animal movement due to the high amount of infrared radiation emitted by living bodies.
Key features:
- Passive operation (no energy emission)
- Sensitivity to skin temperature through black-body radiation
- Effective range of up to 30 feet
- Field of view typically less than 180°
Microwave Sensors
Microwave sensors, also known as Doppler radar sensors, emit continuous waves of microwave radiation and analyze the reflected signals. These sensors detect motion by measuring the frequency shift in the reflected waves caused by moving objects.
Main Characteristics:
- Active sensing technology
- Ability to detect motion through solid objects
- Operational frequency range of 0.3-40 GHz
- High sensitivity to even small movements
Dual Technology Sensors
Dual technology sensors combine two different sensing technologies, typically PIR and microwave, to reduce false alarms and improve detection accuracy. These sensors require both technologies to be triggered before activating an alarm or response.
Key Benefits:
- Reduced false alarms
- Improved performance in challenging environments
- Enhanced reliability in various weather conditions
Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sound waves (above human hearing range) and measure the time it takes for the waves to bounce back from objects. These sensors are particularly effective at detecting motion in three dimensions.
Key features:
- Non-contact sensing capability
- Ability to detect transparent objects
- Typical frequency range of 23-40 kHz
- Effective in both indoor and outdoor settings. If you need further information or have another topic in mind that you'd like structured in a similar way, feel free to let me know!
Tomographic Motion Detectors
Tomographic motion detectors use a network of radio wave sensors to create a "mesh" of detection zones. These sensors can detect movement through walls and other obstructions, making them ideal for large area coverage.
Main Advantages:
- Ability to cover extensive areas
- Detection through walls and obstructions
- Reduced blind spots compared to traditional sensors
Optical Motion Sensors
Optical motion sensors use digital cameras and sophisticated software algorithms to detect movement in their field of view. These sensors can provide detailed information about the size, shape, and direction of moving objects.
Key Benefits:
- High-resolution detection capabilities
- Ability to distinguish between different types of movement
- Integration with video surveillance systems
Vibration Sensors
Vibration sensors detect movement by measuring mechanical vibrations or changes in acceleration. These sensors are particularly useful in applications where traditional motion sensors may not be effective, such as monitoring machinery or detecting intrusions through physical barriers.
Main applications:
- Industrial equipment monitoring
- Structural health monitoring in buildings
- Vehicle security systems
AI-Enhanced Motion Detection
The latest advancement in motion sensing technology involves the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with traditional sensor types. AI-enhanced motion detection systems can analyze complex patterns of movement, distinguish between different objects, and even predict potential security threats.
Main Advantages:
- Improved accuracy in threat detection
- Reduced false alarms
- Advanced analytics for behavior pattern recognition
By understanding the various types of motion sensors and their unique capabilities, one can choose the most appropriate technology for specific applications, whether it's home security, industrial automation, or smart building management. Each sensor type has its strengths and limitations, and often a combination of different technologies provides the most comprehensive and reliable motion detection solution.
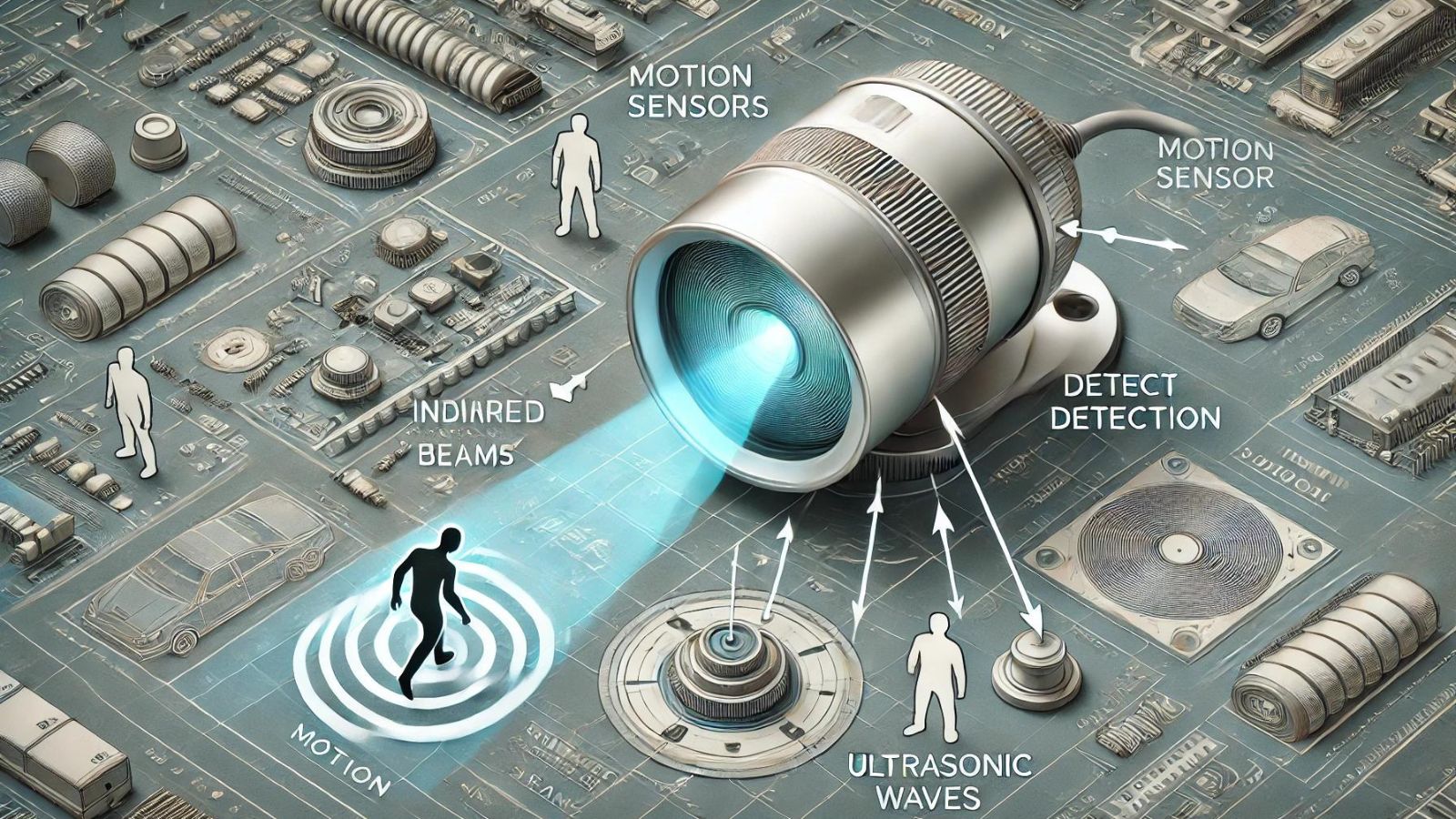
How Motion Sensors Work
Motion sensors are sophisticated devices that detect changes in their environment to trigger specific actions. These sensors employ various detection mechanisms, process signals, and initiate responses based on the detected motion. Let's explore how different types of motion sensors function.
Detection Mechanisms
Motion sensors utilize diverse technologies to identify movement in their vicinity. The two most widely used types are active ultrasonic sensors and passive infrared (PIR) sensors.
Active ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sound waves above the range of human hearing. These waves bounce off objects in the immediate area and return to the sensor. A transducer within the device acts as both transmitter and receiver, sending out the pulse and capturing the echo. The sensor calculates the distance between itself and the target by measuring the time elapsed between sending and receiving the signal.
Passive infrared sensors, on the other hand, detect fluctuations in infrared energy emitted by humans, animals, and objects as heat. PIR sensors are more complex than their ultrasonic counterparts but serve a similar purpose. They can detect the presence of a person or object by identifying changes in temperature within a given area.
Some motion sensors combine multiple technologies to enhance detection accuracy. These "dual technology" sensors often integrate active ultrasonic and PIR sensors into a single unit, improving overall performance and reducing false alarms.
Signal Processing
Once a motion sensor detects a change in its environment, it must process the received signals to determine if an alert is necessary. This process involves sophisticated algorithms and filtering techniques to distinguish between normal environmental fluctuations and genuine motion events.
Multiresolution filtering is a key technique used in motion signal processing. This method applies a cascade of filters to the incoming signal, producing a set of short-time bandpass or lowpass signal components. By recursively filtering and downsampling these components, the system can efficiently analyze the motion data at different frequency levels.
The principle behind this approach is that low frequencies contain general, gross motion patterns, while high frequencies encompass detail, subtleties, and potential noise. By separating these frequency bands, the sensor can more accurately interpret the detected motion and reduce false alarms caused by minor environmental changes.
Triggering Actions
When a motion sensor determines that significant movement has occurred, it triggers a predefined action. In security systems, this typically involves sending an alert to the central control unit, which may then notify the property owner or security personnel.
Modern motion sensor systems often integrate with smart home technology, allowing for more sophisticated responses. For example, when motion is detected, the system might:
- Activate lights in specific areas of a building
- Initiate video recording on connected security cameras
- Send real-time notifications to the owner's mobile device
- Adjust heating or cooling systems based on occupancy
The sensitivity and response of motion sensors can often be customized to suit specific environments and user preferences. This customization helps minimize false alarms while ensuring that genuine security threats are promptly identified and addressed.
In applications beyond security, such as traffic monitoring or environmental observation, motion sensors can trigger data collection processes or alert systems when specific movement patterns are detected. This capability makes them valuable tools in a wide range of fields, from urban planning to ecological research.
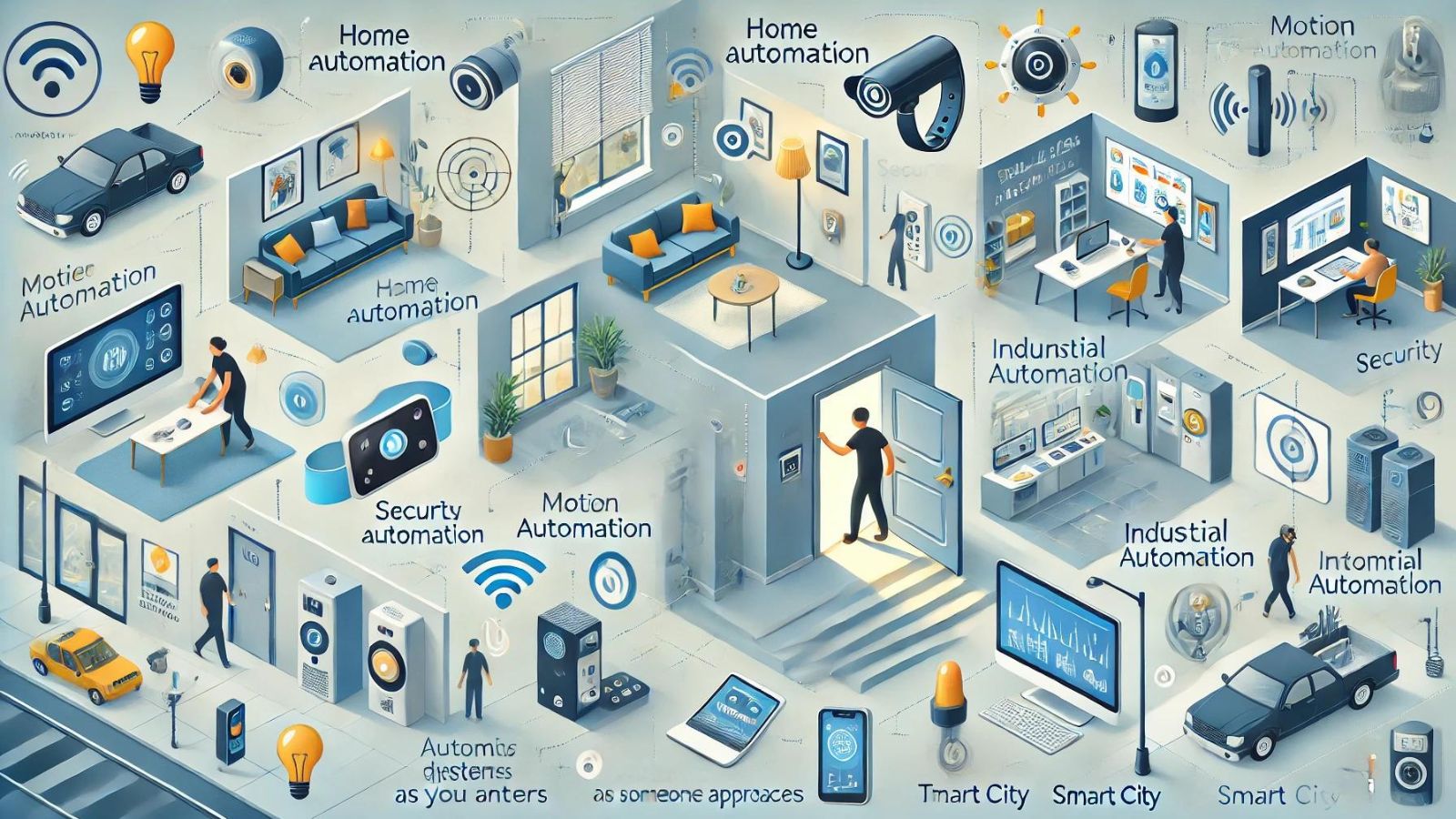
Applications of Motion Sensors
Motion sensors have become integral components in various fields, enhancing security, efficiency, and convenience across different industries. These versatile devices detect and measure movement, converting it into actionable signals. Let's explore some key applications of motion sensors in different sectors.
Home Security Systems
Motion sensors serve as the principal guards of perimeter security, forming the outer layer of protection in home security systems. They offer several advantages:
- Early warning: Motion sensors can alert homeowners to act before a situation escalates, allowing them to call the police before property damage occurs or lives are put at risk.
- Discreet installation: Due to their small size, motion sensors are less detectable than video surveillance systems, making it harder for intruders to locate and disable them.
- Versatile response: When triggered, motion sensors can activate cameras to record events, turn on lights to deter intruders, sound alarms, and even lock doors to contain threats.
Smart Home Automation
In smart homes, motion sensors play a crucial role in automating various systems, enhancing both convenience and energy efficiency:
- Smart lighting: Sensors can be linked to lighting systems, automatically turning lights on or off based on detected motion. This not only improves convenience but also contributes to energy conservation.
- Energy management: Motion sensors can control smart devices like thermostats and appliances. For example, when no motion is detected in a room, the sensor can signal the thermostat to adjust temperature settings or instruct smart plugs to turn off energy-consuming devices.
- Convenience features: Motion sensors can automate various aspects of daily life, such as opening doors or activating household appliances based on detected movement.
Industrial and Commercial Uses
Motion sensors find extensive applications in industrial and commercial settings:
- Security and access control: In large commercial properties or high-security facilities, motion detectors provide instant responses to intruders. They can be integrated with access control systems to send real-time alerts to security personnel.
- Energy efficiency: In office buildings, motion sensors can optimize energy usage by controlling lighting and HVAC systems based on occupancy.
- Inventory management: In retail environments, motion sensors can help track customer movement patterns and optimize store layouts.
Healthcare and Assisted Living
Motion sensors play a vital role in healthcare and assisted living environments:
- Patient monitoring: In hospitals and care facilities, motion sensors can help staff monitor patient movement and detect falls or other emergencies.
- Home care solutions: For seniors living independently, motion sensors can track their status and whereabouts. If unusual lack of movement is detected, the system can alert relatives or caregivers of a possible emergency.
- Vital sign monitoring: Advanced motion sensors are being developed to detect subtle body motions, potentially allowing for non-invasive estimation of heart rate and respiratory rate.
|
Application |
Key Benefits |
| Home Security | Early warning, discreet installation, versatile response |
| Smart Home | Energy efficiency, automated lighting, convenience |
| Industrial/Commercial | Access control, energy optimization, inventory management |
| Healthcare | Patient monitoring, fall detection, vital sign estimation |
As technology continues to advance, the applications of motion sensors are likely to expand further, offering even more sophisticated solutions across various sectors. From enhancing security to improving energy efficiency and healthcare monitoring, motion sensors are shaping the future of smart, responsive environments.
Conclusion
Motion sensors have become game-changers in various fields, from home security to healthcare. Their ability to detect movement and trigger responses has led to significant advancements in safety, energy efficiency, and automation. The diverse types of motion sensors, including PIR, microwave, and ultrasonic sensors, each bring unique strengths to different applications, showcasing the versatility of this technology.
As we look to the future, motion sensors are set to play an even bigger role in shaping smart, responsive environments. Their integration with AI and other cutting-edge technologies promises to open up new possibilities to enhance our daily lives. From improving security systems to enabling more efficient energy use and supporting healthcare monitoring, motion sensors are at the forefront of creating safer, more comfortable, and more connected spaces for us all.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q. What are the different kinds of motion sensors available?
There are several types of motion sensors to consider depending on your needs. Popular options include Passive Infrared (PIR) sensors, microwave sensors, and dual-technology sensors, which utilize a combination of technologies to enhance detection accuracy.
Q. How are motion sensors utilized in various settings?
Motion sensors have a wide range of applications. They are commonly used to trigger automatic door systems in commercial and public buildings. Additionally, they serve as an alternative to occupancy sensors for controlling outdoor and indoor lighting in areas like streets, lobbies, and staircases.
Q. Which sensor is predominantly used for detecting motion?
The Passive Infrared (PIR) sensor is the most frequently used type of motion sensor in commercial environments due to its reliability and cost-effectiveness. PIR sensors are highly regarded for their precise motion detection capabilities.
